Spark Plug Maintenance
Whether you own a lawnmower, weed eater or power generator for motorcycles, the spark plug is necessary for a spark ignition engine to run efficiently. It serves as an intermediary between the ignition system and combustion chamber. It passes electric current from the ignition system to the combustion chamber, so as to aid the combustion of the fuel-air composition and spark plug maintenance is critical to long engine life.
This guide focuses on the spark plug maintenance alongside its functions, life span, faulty plug indicators, and the process of replacing a damaged spark plug.
Functions of a Spark Plug
As mentioned earlier, the spark plug serves a means of transferring electric current in spark ignition engines. However, it can also be used in other systems such as the Saab direct ignition automobile, furnace systems, and ionization measurement.
In Spark Ignition Engines:
The spark ignition engine is also known as a SI engine. The SI engine relies on the exothermic reaction of the gas-air mixture to power itself. And the spark plug is the key to incite the combustion process.
The primary fuel used in spark ignition engines is petrol (gasoline) while diesel engines rely on the compression-ignition process.
Unlike the spark ignition model, compression-ignition engines do not need a spark plug to light up the combustion process. As its name implies, compression-ignition exploits pressure and heat, in order to start the combustion process. Good examples of spark ignition engines are most gasoline powered automobiles, lawnmowers, power generators for motorcycles, and weed eaters.
In Saab Direct Ignition:
The Saab direct ignition was developed by Saab Automobile, a Swedish auto manufacturer. The model depends on capacitor discharge ignition to power up its engine. However, spark plug is used as an alternative when the Saab automobile fails to ignite.
In Furnace Systems:
The furnace, a machine used in the heating and melting of metal ore, could depend on electricity or induction heating. The spark plug is instrumental to the efficiency of an electric furnace. It is often referred to as a flame igniter.
Ionization measurement:
The cam phase, misfire measurement setup, and knock sensor are often used to measure ionic current in cylinders. But when these options are unavailable, the spark plug can be used for ionization measurement.

How to examine a spark plug?
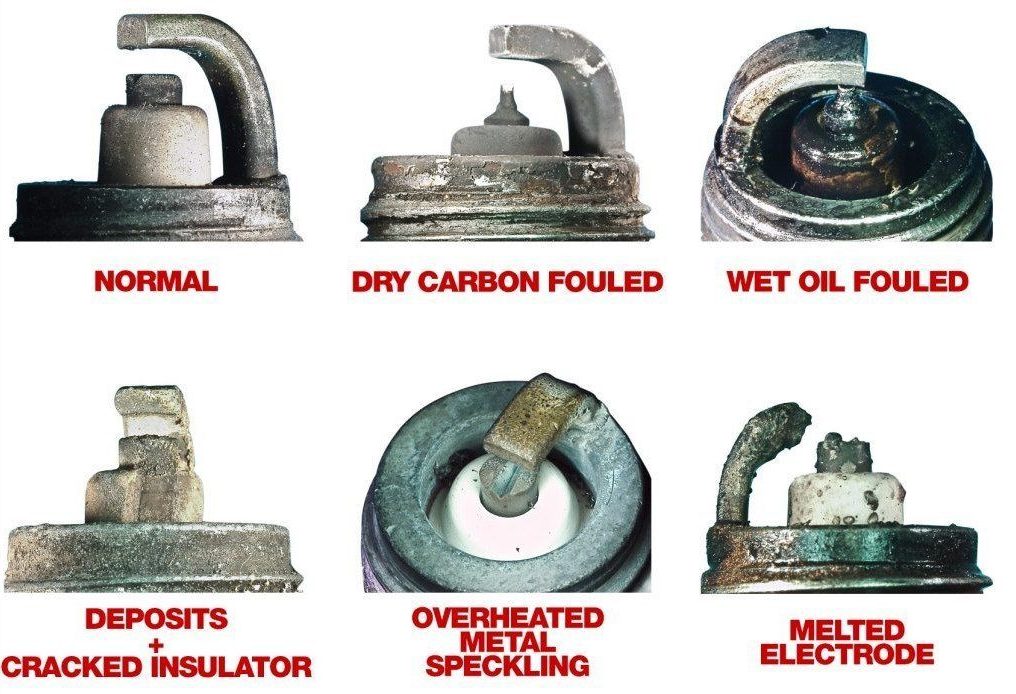
A critical part of spark plug maintenance is examining or 'reading' spark plugs. This examination is one of the various ways of detecting if your engine is working properly. For instance, a professional automotive technician can closely guess the engine’s performance by checking the color and condition around the insulator firing nose.
In this section, you’re going to learn about the indicators to look out for while “reading” your spark plug. Below are the indicators to watch out for and their corresponding implications;
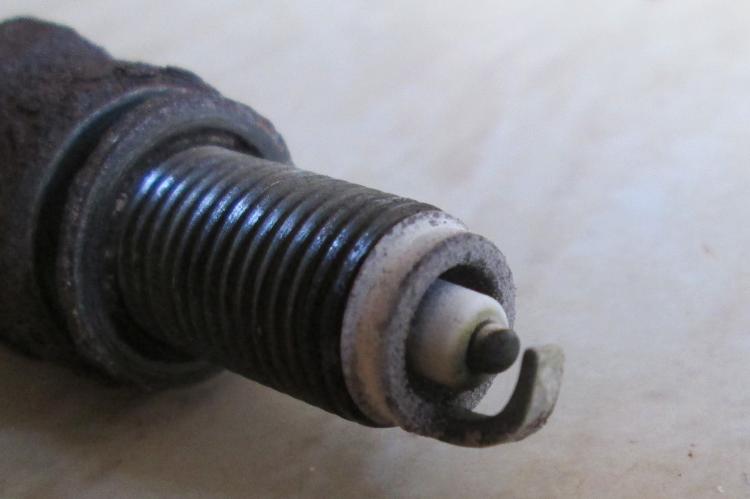

Indicator 1: light gray/tan color
Implication: The light gray/tan color indicates that the engine is functioning well. Every engine in its normal state could give your plug tip a light gray/tan color.

Indicator 2: unusual erosion
Implication: The unusual erosion indicator is defined with a wet-black stain around the plug. It is often a result of corrosion and oxidation around the electrode area. When oxidized, it could give off green stains alongside the dark fouling. After removing the spark plug, check if it has a messy and fretted surface. Another type of erosion is lead erosion.
Indicator 3: lead stain
Implication: The lead stain or lead erosion is defined with a depreciating ground electrode alongside a chipped tip. It is as a result of the escape of lead compounds from the gasoline, which combines with the components of the electrode (primarily nickel alloy) at extreme temperatures. With time, the lead elements start permeating causing the plug to be damaged.
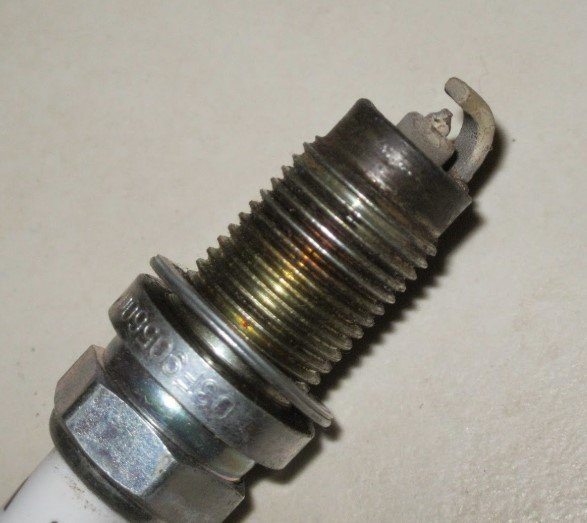

Indicator 4: dry stain
Implication: Dry stain could be a consequence of the reduction in insulation resistance, which paves way for the accumulation of dry carbon materials. Sometimes, the carbon deposits might be wet.
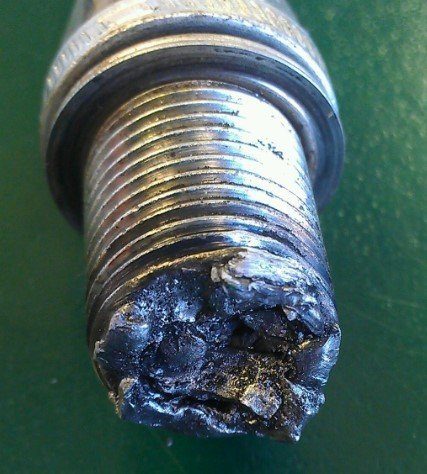

Indicator 5: breakage or melting
Implication: secondary school physics gives us an insight into the negative effects of thermal expansion. We can apply the same knowledge when it comes to plug breakage. When a plug tip is exposed to consistent thermal expansion and thermal shock due to the temperature instability, it would break. While breakage is a result of thermal expansion, melting is a consequence of overheating. Melting causes the electrode surface to become lustrous and odd.
What is The Average lifespan of a Spark Plug?
The lifespan really depends on spark plug maintenance. Studies show that a car spark plug can last for about 10,000 miles to 30,000 miles on average. Also, the quality and brand is a huge determinant.
Some spark plugs have been rumored to last for up to 185,000 miles or more. The trick is to keep gaping them (for wear) every now and then. The same rule may not apply to lawn mowers and weed eaters, as the electrical load and working hours varies significantly.

Long Term Disadvantages of Using a Faulty Spark Plug
The disadvantages discussed under this section were inferred using a car. But they can occur in other spark ignition engines, as the makeup of every fuel-air engine is fundamentally similar. Below are the symptoms associated with a bad spark plug and are conducive to a lack of spark plug maintenance:
Engine Misfires:
A misfire is a failure in sequence, in this case, ignition sequence. There are various causes of engine misfire and a faulty plug could be the reason your engine is misfiring. Misfires do occur while starting the engine or gearing up. Read more about engine misfires.
Immense Combustion of Gas:
A bad spark plug could increase the amount of fuel exhausted by the engine. On an average day, an engine that uses roughly 6 gallons of fuel could start using 8 gallons. Such increase in fuel consumption overheats the engine and causes the spark plug to melt.
Engine Backfire:
There’s a difference between an engine backfire and engine misfire. The most obvious difference is that an engine backfire occurs when an engine is running and is a rather loud, while misfires usually occur under a load and can be quite subtle. An engine backfire is an unexpected explosion that takes place in the exhaust system of a running engine.
The combustion, which is meant to happen inside the combustion chamber, is observed in the exhaust system. An engine backfire could also be linked to an unbalanced fuel-air ratio and overheating. As we’ve noted earlier, one of the causes of overheating is a faulty spark plug. Failure to replace it, can lead to catalytic converter damage.
Lack of Acceleration:
Engine ignition and acceleration go hand in hand. Failure to ignite fuel-air mixture would make combustion impossible, ceasing all forms of acceleration. You would normally not be worried about such events as a sudden lack of acceleration, if you do check on spark plugs (and other parts of the engine) on a regular basis and during routine maintenance procedures.
Off the line power might suffer up to a 40% power reduction or total loss of acceleration depending on the condition of the spark plug. It is also necessary to pay attention to the time it takes for your engine to start. If you’re experiencing multiple misfires before the engine starts, then, you have to service your plugs or replace them.
Excessive Exhaust Output:
An increase in exhaust emissions is bad for you and the environment. That’s the reason government agencies often impose emission restrictions on heavy machine operators. A faulty spark plug or imbalanced gas-air mixture could increase the exhaust output, endangering the biological and atmospheric environment.
Engine Knocking:
The spark plug ignition is meant to be the primary source of ignition in the combustion process. However, when the process is skipped, it results in an irregular explosion.
The zenith of the combustion process is supposed to be a product of maximum optimization of the four-stroke cycle, a cycle observed by the engine while rolling the crankshaft. Engine knocking is defined as a metallic pinging sound that is traced to a shock wave from an explosion in the engine.
It’s necessary to note that pre-ignition and knocking are not the same, however, the latter might follow the former. A bad spark plug is a possible cause of engine knocking.
In fact, you should take it seriously once it gets really audible. Consistent engine knocking can cause mechanical damage. It’s better to change a faulty plug than to change other expensive parts of the engine.
Curious to learn more? Read our more in depth article here.

How to remove a Spark Plug
During repair or an engine check, the spark plug can be damaged regardless of its size or brand. The damage can be caused due to the application of excessive force or cross-threading. Sometimes, the spark plug could get damaged without external interference. The next thing to do is to remove the damaged plug.
Engine manufacturers often provide spark plug maintenance tool kits. In case you misplace your kit, you can always order for a new spark plug maintenance kit online or offline.
If your spark plug is badly damaged and normal removal is not an option, there are two types of easy-out tools used for plug removal, namely; spiral-cut and square-cut. It is advisable to use the square-cut instead of the spiral-cause, since the spiral-cut has a higher tendency of expanding the shell and making the job more complicated as you apply more force. The square-cut type is perfectly designed to remove a spark plug, as it holds firm to the strong part without damaging the shell metal.
Otherwise, removing the spark plug should be a very easy task. You should be done within minutes. If the plug requires excessive effort to remove, it means the person who last installed it, applied too much force or the plug area has not been serviced for a very long time.
Follow these steps to properly remove the faulty spark plug
- Turn the engine off, if it is on. Never remove the plug of an engine while it’s still on for safety reasons.
- Ensure the engine cools down before proceeding.
- Remove the plug wire/cover and use a towel or rag to remove the dirt and oil around the spark plug area.
- Use of a penetrating rust spray or oil to ease the removal can be beneficial, if the spark plug is too tough. For spark plugs that were not installed with excessive force or deprived of servicing, you might not need to add penetrating lubricants.
- Wait for the penetrating spray to ease the frictional forces by dissolving rust and corrosion for a couple of minutes or longer. Then, using the correct spark plug socket, extension and ratchet or bar, begin by applying steady force.
- If an easy out is necessary, be sure to use the correct setup and be steady as you turn the easy out in a counterclockwise direction until you remove it.
How to check for a faulty Spark Plug
To remove a spark plug, follow the instructions given above. This section gives you an idea of what and where to check for anomalies in the spark plug.
After removing the spark plug, clean it with a rag to get a perfect view of its parts. See if there’s any sign of broken or cracked porcelain, melted electrodes or hard-to-remove deposits. The deposits could be caused by carbon or misfiring. If you find any of the three indicators, you should replace the spark plug.
Also, check the spark plug gap and adjust if necessary. Some spark plugs come with limited re-adjustment features, but it’s wise to confirm if the gap is in good shape. It is important to note that some deposits are removable and may not warrant replacement. Such deposits can be removed using a spray-on plug cleaner or any soft brush. Carefully scrape off the dry deposits with a sturdy knife.
For unbroken spark plugs, you can continue to use them, but they must be clean. Be careful while installing the plugs and do not apply excessive force. Once you’re done, replace the spark plug wire/cover, then start your engine to see if all is in order.
About the Author
Tech Guy
Automotive enthusiast, passionate about Jeeps, hot-rods, turbos, performance, efficiency, diesels, fuels, high performance oils, additives and anything with an engine.